Linux is a family of open-source Unix-like operating systems based on the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released on September 17, 1991, by Linus Torvalds.
An Operating System is the software that directly manages a system's hardware and resources, like CPU, memory, and storage. The OS sits between applications and hardware and makes the connections between all of your software and the physical resources that do the work.
To store the data or process the data (add / remove / move/ execute scripts) into the Hadoop, Data Analyst has to do through Edge Node / Gateway which is Linux OS.
So, Big Data Developers need to know at
least 20 Linux Commands, while ETL Developers need to know 50 to 60 Linux
Commands.
But most People inclined towards Windows OS because of powerful User Interface (UI) than Linux OS UI.
In Real time Cluster creations, we use Linux OS
because of Security and Compatibility.
We need to perform Linux commands in CLOUDERA
distribution which needs to be installed along with VMware Workstation 16
Player.
Ctrl L – to refresh Cloudera screen.
Anything
starts with
d – Directory
(folder)
-r –
file (store data)
Landing
Layer is “/home/cloudera” which is Home
Path for Local File System [LFS].
2) mkdir [Make Directory]
Create a Directory of a File as example Class10 (Folder).
4) ll [Long Listing]
ll Shows the file complete details with date and time.
Mostly Hidden files are related to
configuration property used in SQOOP.
Example File name is Hadoop_information.txt
Press
“Escape
I” to type the data – You will see INSERT at the bottom.
After above step, press ESCAPE and
give command “:wq!” At the bottom,
your information is saved.
Create another File “Hadoop_data.txt” in same Directory
Class10 which already has “Hadoop_information.txt” using command steps 9 &
10.
1113) cp [Copy File from one to another]
This command tells how to copy the content from file “hadoop_data.txt” to “Hadoop_backup.txt”.
14) Concat (cat >)
And instead of “cp”, you can also give “cat
>” command to copy the file in real time.
15) Append (cat >>)
If
you add more greater than such as cat>>,
then data will append (addition / duplicate).
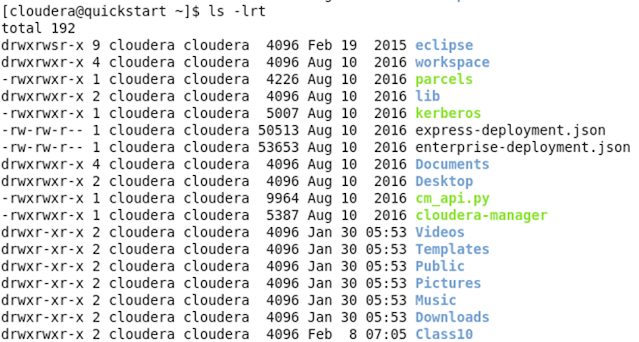
Now press Ctrl L for Refresh and type ls –lrt command.
19) history [to check all previous commands]
|
LINUX |
|
|
Commands |
Meaning |
|
PWD |
Present
Working Directory |
|
mkdir |
Make
Directory |
|
ls |
Listing |
|
ll |
Long
Lising |
|
ls -lrt |
Increasing
Output of Listing |
|
ls -lart |
Hidden
Files |
|
cd |
Change
Directory / got to Home Path |
|
touch |
Create
Empty File |
|
vi |
Open the
File |
|
:wq! |
Save the
File |
|
cat |
Read
data inside the file |
|
rm |
Remove
the File. |
|
cp |
Copy file
from one to another |
|
cat > |
Concat |
|
cat
>> |
Append |
|
wc -l |
Word
Count lines |
|
head |
to read
beginning lines of data in a file. |
|
tail |
to read
last lines of data in a file. |
|
history |
all
commands |
|
mv |
Move
file |
|
grep |
Display particular
number lines |
|
comm |
difference
between files |
|
sed |
Stream
Editor for Substitution |
|
top |
to check
CPU usage |





























No comments:
Post a Comment