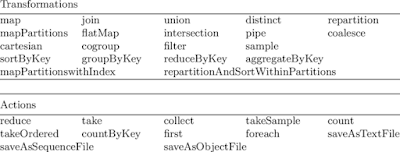
The RANK() function is also known as window function that assigns a rank to each row within a group of data sets. The rank of a row is determined by one plus the number of ranks that come before it.
The
syntax of the RANK() function is as follows
SELECT column_name,
RANK()
OVER (PARTITION BY... ORDER BY...) as rank
FROM table_name;
In this
syntax:
The column_name represents the column that you wish
to rank in the table
The
PARTITION BY clause divides the result set's rows into partitions based on one
or more parameters
The ORDER
BY clause sorts the rows in each partition where the function is applied
RANK() function is used as part of the SELECT statement.
Basically, you add another column to your result
set. This column includes the rank of each record based on the order specified
after the ORDER BY keyword.
This entails specifying (1) the column to use for sorting the rows and
(2) whether the order should be ascending or descending.
The first row gets rank 1, and the following rows
get higher rankings. If any rows have the same value in the column used for
ordering, they are ranked the same. The RANK() function
leaves gaps in such cases.